Section: New Results
Fast Regularized Ensembles of Models
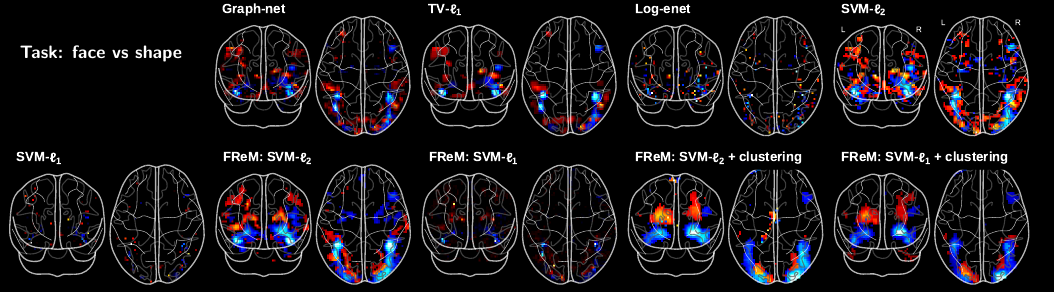
Brain decoding relates behavior to brain activity through predictive models. These are also used to identify brain regions involved in the cognitive operations related to the observed behavior. Training such multivariate models is a high-dimensional statistical problem that calls for suitable priors. State of the art priors –eg small total-variation– enforce spatial structure on the maps to stabilize them and improve prediction. However, they come with a hefty computational cost. We build upon very fast dimension reduction with spatial structure and model ensembling to achieve decoders that are fast on large datasets and increase the stability of the predictions and the maps. Our approach, fast regularized ensemble of models (FReM), includes an implicit spatial regularization by using a voxel grouping with a fast clustering algorithm. In addition, it aggregates different estimators obtained across splits of a cross-validation loop, each time keeping the best possible model. Experiments on a large number of brain imaging datasets show that our combination of voxel clustering and model ensembling improves decoding maps stability and reduces the variance of prediction accuracy. Importantly, our method requires less samples than state-of-the-art methods to achieve a given level of prediction accuracy. Finally, FreM is highly parallelizable, and has lower computation cost than other spatially-regularized methods.
More information can be found in Fig. 5 in [23].
|